Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is goal oriented psychotherapy. It takes a practical approach to problem-solving. We have developed patterns of thinking and behaving over our lifespan. CBT can offer tools to work on changing those patterns of thinking and behaving which helps us to then change the way that we feel.
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT)
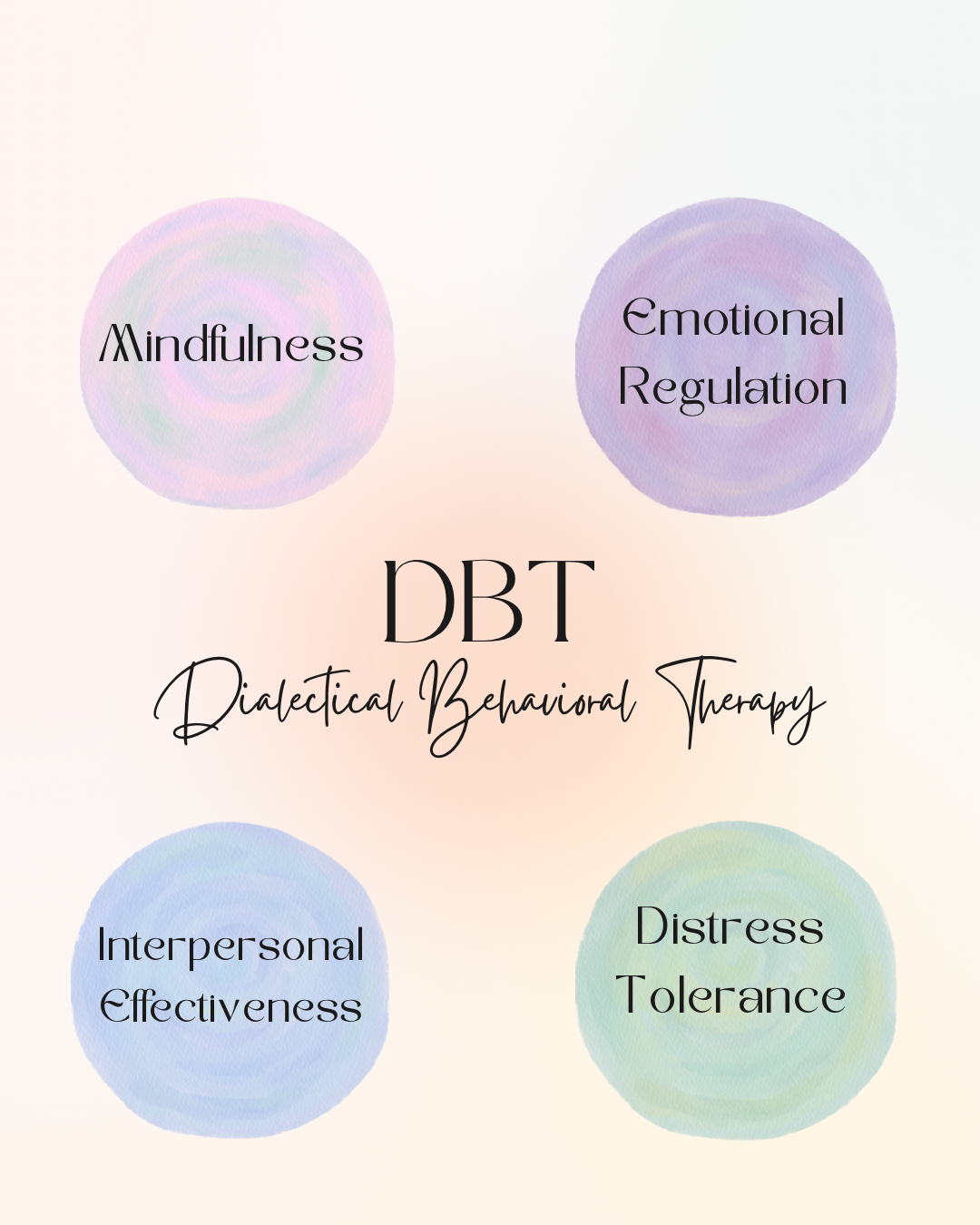
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) is very similar to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and implements similar techniques. Dialectical means the integration of opposites. It helps to get us away from extreme positions which can leave us feeling stuck. We work to assess situations and identify behaviors that are not effective or relevant. Through DBT, we focus on four main areas including mindfulness, emotional regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, and distress tolerance.
Solution-Focused Therapy

Solution-Focused Therapy (SFT) empowers you to utilize your own abilities and strengths to solve problems. This can be very different than ‘traditional’ psychotherapy because the focus is on goals and problem-solving.
Mindfulness-Based Practices

Mindfulness involves having moment to moment awareness of our thoughts, feelings, environment, and bodily sensations. The focus is on acceptance without judgement. It allows us to focus on the here and now without being stuck in the past or fantasizing about our future.
Strength-Based Approach

The strength-based approach has its foundation in social work and builds upon the client’s strengths, specifically seeing the client as resourceful and resilient when they are in adverse conditions (Strengths-Based Models in Social Work; McCashen, Wayne [2005]). A unique characteristic of this approach is that it is client led and is centered on outcomes using an individual’s future set of strengths.
Trauma-Informed Care

Trauma-informed care is a strengths based framework that is grounded in an understanding of and responsiveness to the impact of trauma, that emphasizes physical, psychological, and emotional safety for both providers and survivors, and that creates opportunities for survivors to rebuild a sense of control and empowerment.”

